There comes a time in every company’s journey when the realities of scale become impossible to ignore.
Suddenly, your business has gone from a single salesperson to a team of hundreds, each with a different approach to selling — and not all of them are right for your needs. But to succeed, you’ll need your team to execute your go-to-market strategy in a single, unified motion. How can you unite many sellers under one approach?
Enter sales methodologies. Businesses rely on these frameworks to help their reps consistently deliver at every stage of the sales cycle. If your sales organization is growing fast, now is the time to explore investing in one.
In this article, discover 16 sales methodologies, each offering unique advantages tailored to different industries, sales cycles, and customer interactions. The key to choosing lies in understanding which approach aligns best with your business goals and customer needs.
What Is a Sales Methodology?
Sales methodologies outline how your sales team approaches the sales process. They provide a structured set of practices that salespeople use to convert prospects into customers, ensuring consistent, repeatable success at each sales cycle stage.
Sales Process vs. Sales Methodology
Think of the sales process as a sequence of steps to complete a sale, like prospecting, qualifying, and closing. On the other hand, sales methodology provides strategies to support those steps.
Simply put, the process is the “what” of selling, and the methodology is the “how” to approach and execute each step. For instance, if your process includes follow-up calls, the methodology might dictate using a consultative approach to build relationships.
16 Popular Sales Methodologies
Sales methodologies are not all created equal, and you are not limited to using one. When evaluating methodologies, consider your product type, sales cycles, and customer interactions. For example, a methodology might emphasize relationship-building for complex, high-value products. A more transactional approach might work well for routine, lower-cost items.
Read on to learn about the different sales methodologies for B2B sales teams. Choose the most suitable methods for your business and tailor your approach to meet unique customer needs, making both sales reps and prospects happier.
1. Challenger Sales Methodology
Matthew Dixon and Brent Adamson introduced The Challenger Sales model in their 2011 book, “The Challenger Sale: How to Take Control of the Customer Conversation.” This technique teaches sales reps to challenge prospects’ thinking and offer original perspectives. It encourages sales reps to push customers out of their comfort zones and challenge the norm.
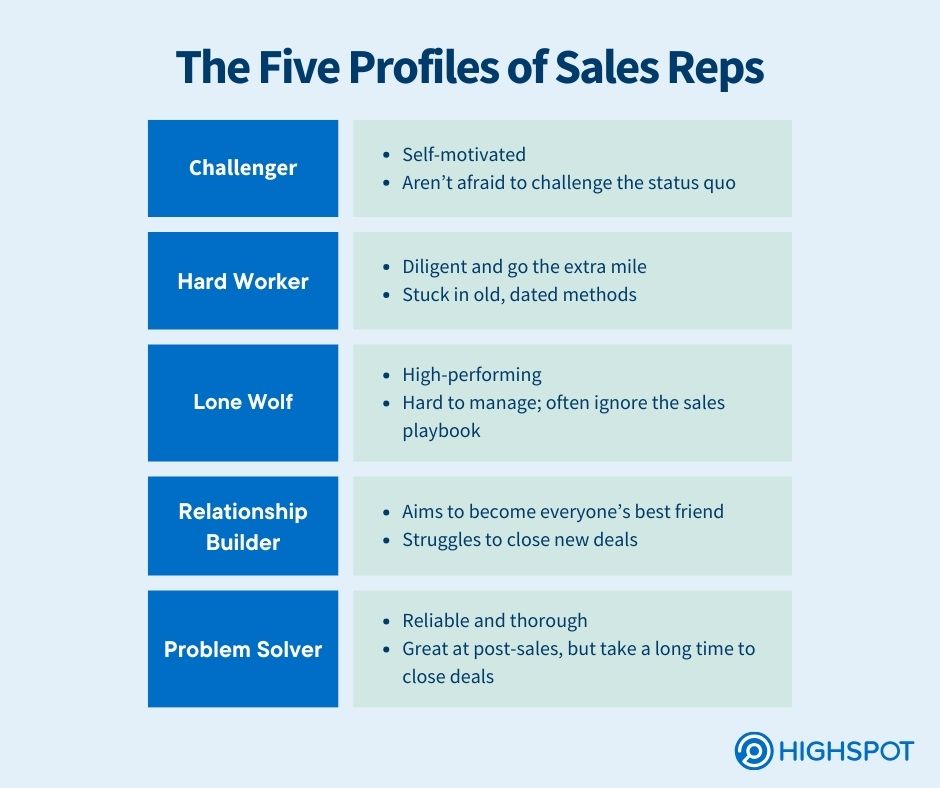
The methodology classifies sellers into five types:
- Challenger: Bold, insightful, and unafraid to push customers out of their comfort zone. They lead with education and drive the biggest deals.
- Hard worker: Puts in the hours, always looking to improve. Gritty but can rely too much on effort over strategy.
- Relationship builder: Builds trust and keeps clients happy. However, they struggle to close new deals as they avoid tough conversations.
- Lone wolf: Independent, confident, and instinct-driven. Can crush sales but resists structure and teamwork.
- Problem solver: Detail-oriented and reliable. Customers love them, but they spend too much time fixing instead of selling.
The “challenger” stands out by deeply understanding the customer’s business and creating constructive tension. They thrive by teaching, tailoring their approach to the customer’s needs, and taking control of the sales conversation. This tension highlights the cost of ‘doing nothing’ and drives the customer towards a decision.
This sales methodology works best in complex sales where clients need a new way of thinking about their problems. It also suits large sales organizations because it keeps deals personalized without restructuring the team.
Pros:
- Encourages reps to teach customers new perspectives
- Often leads to higher close rates and larger deals
- Effective in complex sales environments
Cons:
- Requires thorough training and highly skilled reps
- Can be perceived as aggressive if not executed properly
- May not work well with several industries or customer types
2. Conceptual Selling
Stephen Heiman and Robert Miller developed Conceptual selling. This methodology views sales as convincing buyers to purchase an idea rather than just buying a product.
Salespeople should focus on listening, engaging with compassion, and conducting comprehensive discovery through questioning to understand a customer’s desired outcomes. They then connect the dots between this ideal state and the product’s capabilities.
To do this effectively, sales reps should ask five types of questions:
- Confirmation questions: Make sure you and the buyer are aligned. Reaffirm what you’ve discussed so far and clarify the problem they need to solve.
- Attitude questions: Get to know the buyer beyond their business needs. Understanding their personal priorities, concerns, and decision-making style uncovers their motivations.
- Basic issue questions: Address potential roadblocks before they become problems.
- Commitment questions: Gauge their level of urgency and investment. Are they just exploring options or are they serious about finding a solution?
- New information questions: If any details are unclear or missing, ask targeted questions to fill in the gaps.
This methodology is perfect for businesses whose products must be deeply integrated into a buyer’s strategic operations to generate value. It often excludes products that can be purchased through self-service modules.
Pros:
- Focuses on understanding the customer’s concept of a solution
- Builds strong customer relationships
- Helps align the sales process with the customer’s buying process
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming due to the extensive discovery phases
- May be challenging to implement consistently across a sales team
3. Consultative Selling
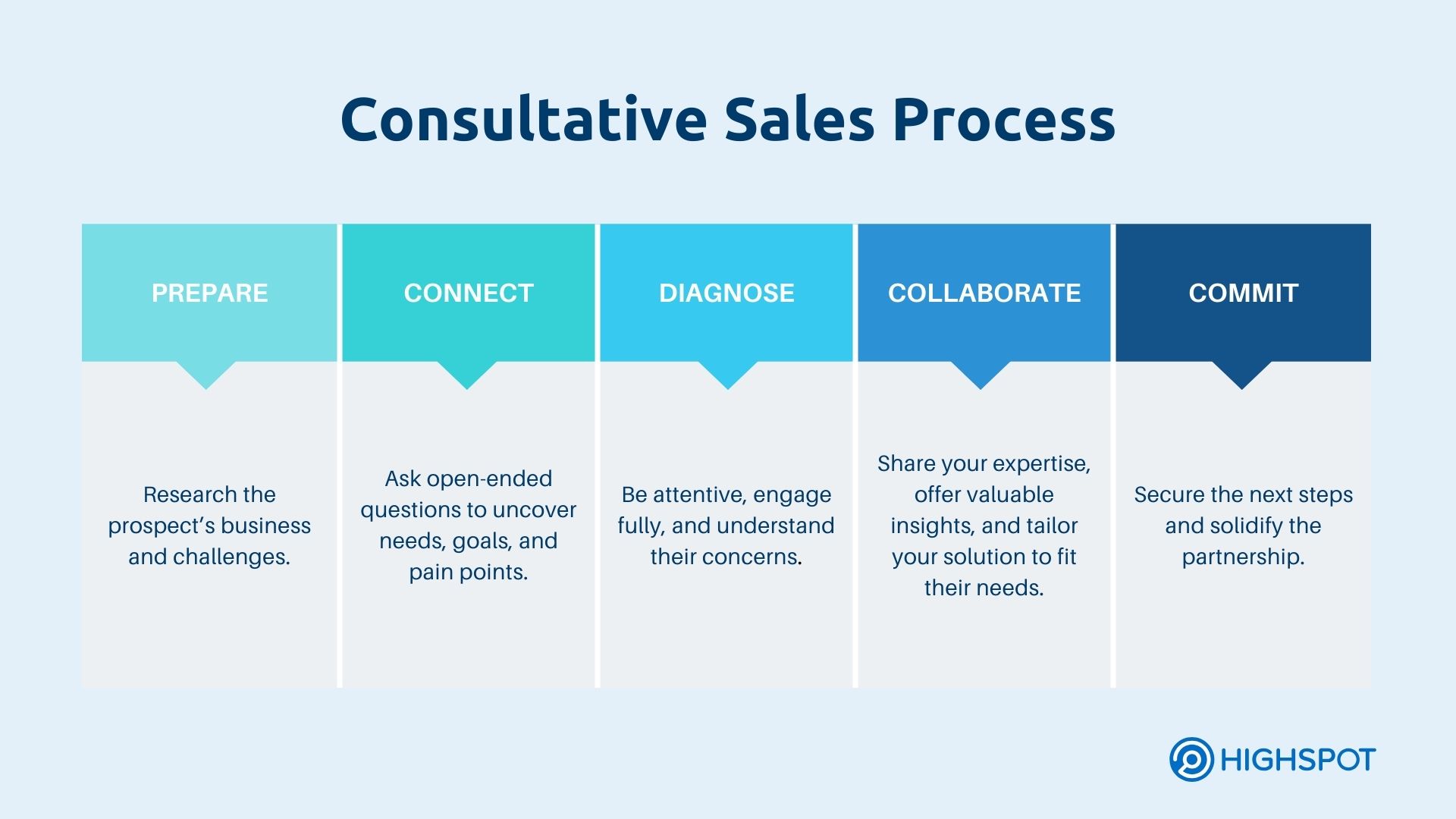
Consultative selling builds relationships and provide customized solutions to customers’ problems. This methodology involves understanding the customer’s needs and acting as a trusted advisor or consultant. It’s effective for complex products and services where the sales process benefits from more personalized hand-holding.
Pros:
- Builds trust and long-term relationships
- It can lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty
Cons:
- Time intensive, requiring thorough research and understanding of the customer
- It may result in longer sales cycles
4. Customer-Centric Selling
Mike Bosworth created customer-centric selling, emphasizing meaningful conversations with prospects to identify needs and determine the best solution. This is achieved using targeted conversation lists—a set of leads marketers and sellers have agreed to target. By focusing on specific accounts and titles, sellers can invest in interactive conversations that address the buyer’s needs and move them toward purchase.
Here are the key components of customer-centric selling:
- Have a conversation, not a presentation
- Ask relevant questions
- Prioritize solutions over relationships
- Engage decision-makers
- Prioritize quality over quantity
- Show product value through real-world use
- Close on the buyer’s timeline
- Empower buyers instead of pushing a sale
This approach is best for companies looking to become deeply embedded within customers’ businesses, requiring tight alignment between marketing and sales teams.
Pros:
- Prioritizes the customer’s needs and goals
- Builds strong, trust-based relationships
- It can lead to higher customer satisfaction and repeat business
Cons:
- It can be time-consuming and resource-intensive
- Requires a deep understanding of the customer’s business
- It may lead to over-customization and decreased efficiency
5. Gap Selling
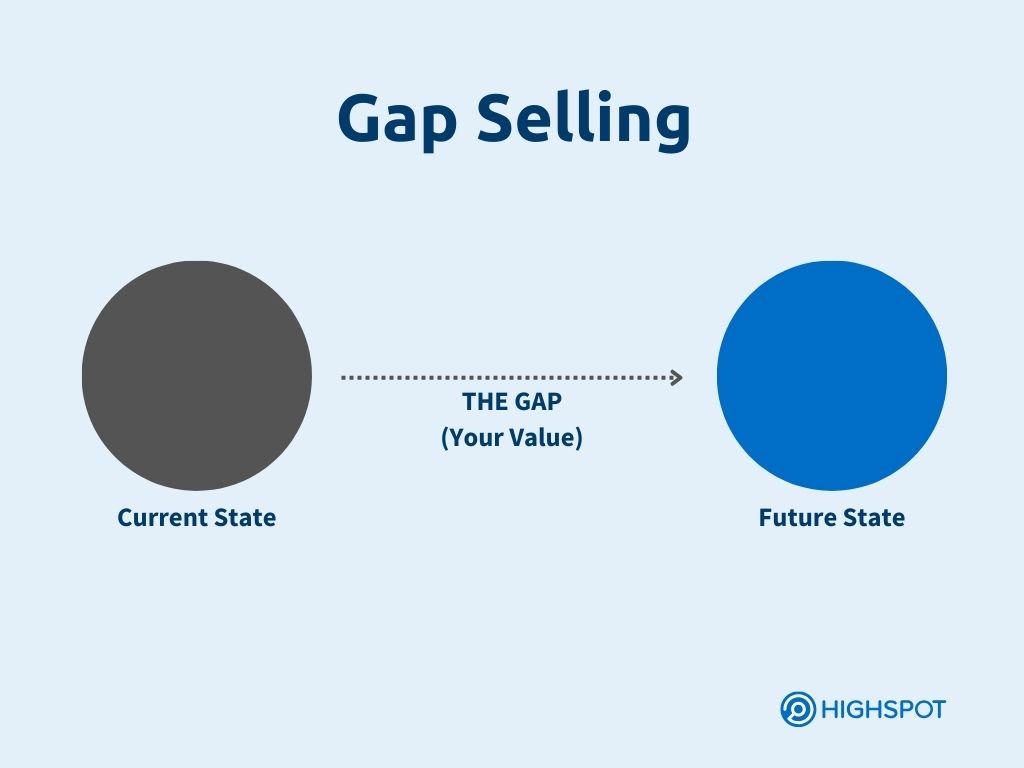
Keenan, CEO and president of A Sales Growth Company, developed Gap selling. It urges sellers to focus on the customer’s problem—identifying the gap between where they are now and where they want to be—then positioning their solution as the bridge to close that gap. This approach shifts the focus from merely selling products to genuinely addressing customer challenges.
Keenan’s methodology argues against the idea that closing skills and overcoming objections define good salespeople. Instead, it highlights the importance of understanding and solving customer problems, leading to shorter sales cycles, increased revenue, higher deal values, and happier buyers.
6. Inbound Selling
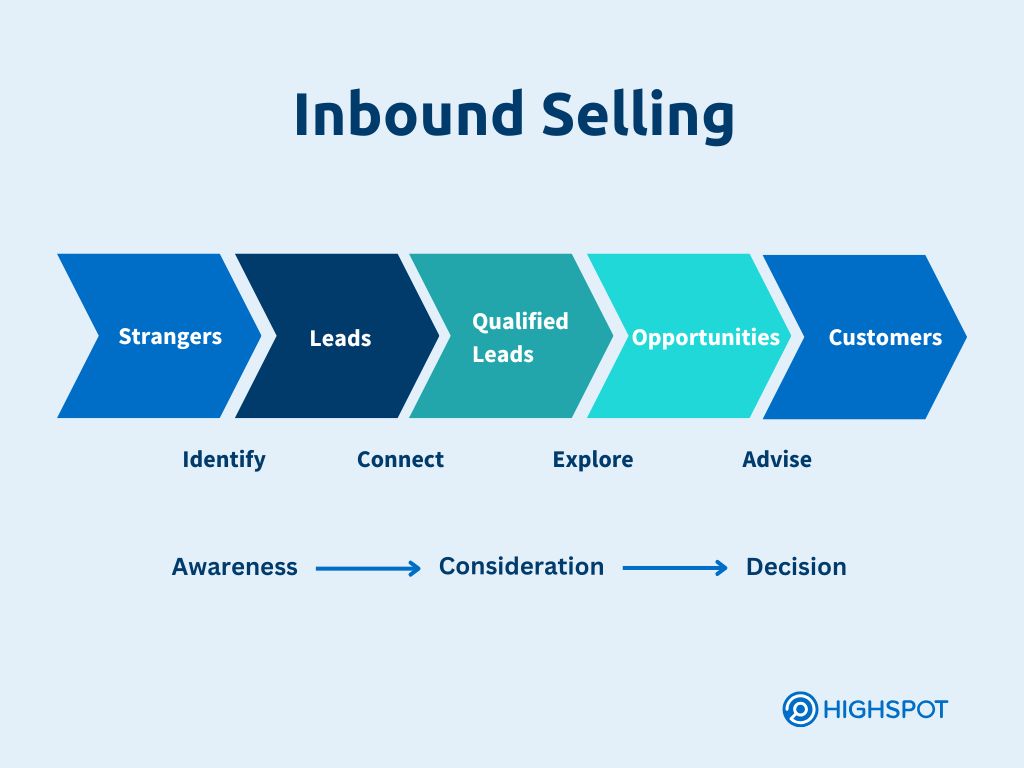
Inbound selling methodology relies on attracting interested buyers and continuous engagement to close deals. This approach focuses on educating them through valuable content and digital media. Salespeople connect buyers with relevant content and engage them across multiple channels, such as social media and in-person events. Over time, they align product offerings with buyer pain points, guiding the deal toward closure.
Inbound sales methodology is best suited for businesses with solid marketing teams that can support SEO, content creation, and demand generation across many channels.
Pros:
- Aligns with modern buyer behavior and preferences
- Attracts customers through valuable content and engagement
Cons:
- Can take time to build up a steady stream of inbound leads
- May not be as effective for short sales cycles or transactional sales
7. MEDDIC
The MEDDIC sales methodology was created in 1996 by Dick Dunkel and Jack Napoli. It focuses on six qualification components:
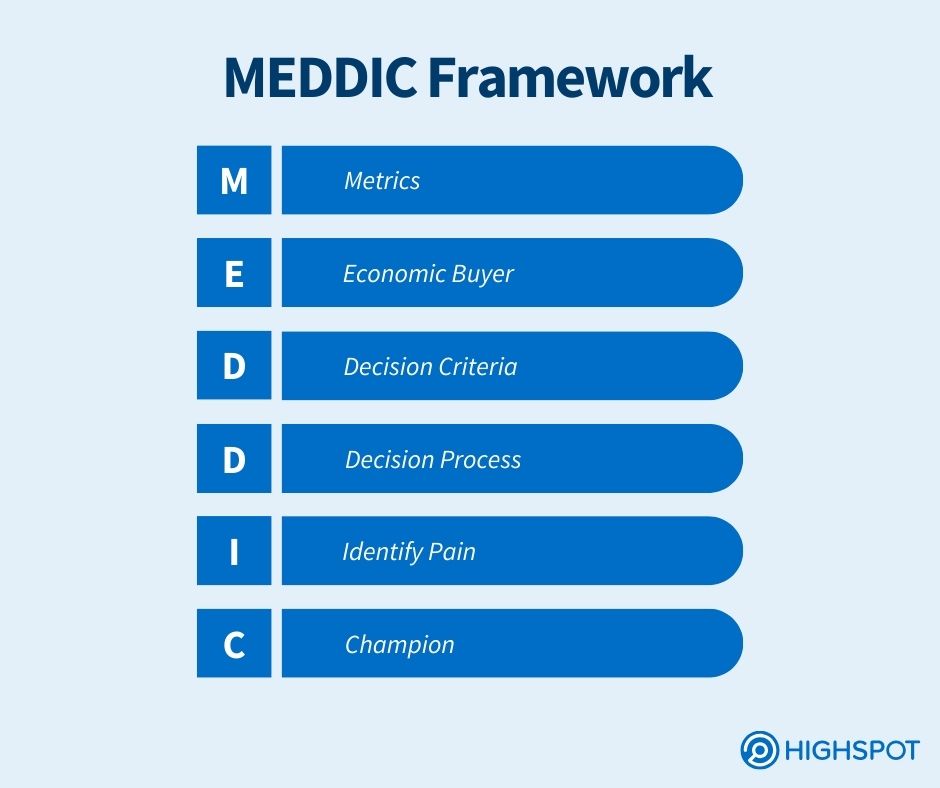
- Understand the prospect’s metrics
- Know the economic buyer or financial authority
- Find the decision criteria and steps in the decision-making process
- Identify the pain the prospect must solve
- Identify the champion.
Salespeople follow the methodology’s guidelines to determine if a buyer fits their product well. If buyers meet the MEDDIC qualifications, the sales rep knows they should dedicate time to close the deal.
This approach is structured to ensure sales reps focus their efforts on the most likely buyers, leading to higher conversion rates and shorter sales cycles. For instance, companies using MEDDIC have reported significant improvements in their sales processes, with some achieving up to a 25% increase in their win rates.
MEDDIC works best for large B2B deals that take time to close. If you are focusing on high-value prospects, this methodology will help you navigate complex deals and get key stakeholders on board at the right time. If you handle many clients, however, this might not be a good fit.
Pros:
- Provides a structured approach to qualifying leads
- Helps ensure alignment with key decision-makers and metrics
- It can lead to more predictable and consistent sales outcomes
Cons:
- Can be seen as rigid and process-heavy
- Requires thorough understanding and adoption by the sales team
- It may be less flexible in dynamic or rapidly changing sales environments
8. N.E.A.T. Selling
Sales Hacker and the Harris Consulting Group came up with N.E.A.T. selling. It’s a modern alternative to traditional sales qualification processes like BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, and Time frame) and ANUM (Authority, Need, Urgency, Money). N.E.A.T stands for:
- Needs: What is the deep, underlying problem the prospect is trying to solve?
- Economic impact: How does solving this problem affect their bottom line? What’s the financial benefit of your solution?
- Access to authority: Is the person you’re speaking with the decision-maker, or do you need to engage others in the buying process?
- Timeline: When does the prospect need a solution in place?
This methodology helps salespeople qualify buyers using a thorough discovery process, allowing them to identify and prioritize hot leads. Sellers focus on connecting product benefits to buyer pain points, demonstrating economic impact, mapping accounts to include decision-makers, and setting a timeline to ensure timely deal closure.
N.E.A.T. is ideal for businesses whose buyers don’t follow a linear customer journey, such as SaaS solution buyers interacting with a brand through multiple digital touchpoints.
Pros:
- Helps prioritize opportunities based on impact and feasibility
- Encourages strategic and value-driven sales conversations
Cons:
- May not be suitable for all sales environments
9. The Sandler® Selling System
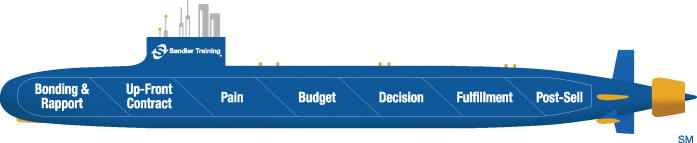
Founded in 1967, the Sandler sales methodology focuses on guiding the sales process collaboratively without high-pressure tactics. It redefines the traditional sales process by emphasizing trust and honest conversations. This methodology stresses meaningful relationships and delivering high-value solutions.
Salespeople position themselves as trusted advisors and view the buyers as equals. Both parties should feel confident and equally invested in ensuring the offer is the right fit.
Initially, sales reps conduct deep discovery sessions to qualify potential buyers. They must tackle common objections—like time or budget—early on. The idea is not to force every deal through, but to understand potential roadblocks ahead so they don’t waste time on leads that aren’t a good fit. Once a lead is deemed qualified, the salesperson sets clear expectations and guides the deal forward while maintaining regular communication.
The Sandler sales methodology suits businesses with complex products requiring a significant investment in the buyer-seller relationship. Positioning sales reps as advisors ensures that customers receive tailored solutions and advice.
Pros:
- Emphasizes qualification and understanding the buyer’s pain points
- Uses a conversational approach that builds trust and rapport
- Provides a systematic framework for managing the selling process
Cons:
- Requires significant training and practice to master
10. SNAP Selling
SNAP Selling, developed by Jill Konrath in 2012, is perfect for today’s buyers with busy schedules. SNAP stands for Simple, iNvaluable, Aligned, and Priority. Konrath realized buyers are swamped with information and have little time to make sense of it all, creating three major hurdles: getting access to decision-makers, sticking to the status quo, and managing the complexity of changes.
To tackle these hurdles, SNAP selling zeroes in on four principles:
- Keep it simple with a clear, straightforward value proposition.
- Be invaluable by offering perspectives and benefits that make your product stand out.
- Ensure your solution is aligned with the buyer’s main goals and needs, making it relevant and urgent.
- Focus on priority, addressing the buyer’s most pressing issues.
SNAP selling intends to make it easier for sales reps to connect with overwhelmed buyers. It is ideal for businesses that need to stand out in a crowded online market. By sticking to the SNAP principles, sellers can cut through the noise of ‘too much information’ and help buyers make an informed decision.
Additionally, the methodology uses a Buyer’s Matrix to map out and understand buyer priorities.
Pros:
- Simplifies the sales process to align with modern buyers
- Focuses on speed and clarity
- Encourages understanding of the buyer’s decision-making process
Cons:
- May oversimplify complex sales
- Requires quick adaptation and responsiveness
11. SPIN Selling
SPIN selling was developed by Huthwaite International and made popular in a 1988 book by Neil Rackham. It incorporates four types of questions: situation, problem, implication, and need-payoff. These questions help sales professionals build a strong case for their solution by understanding their prospects’ needs.
Here’s how it works:
- SPIN sellers start by asking situation questions to understand the prospect’s current situation.
- They move on to problem questions to identify the prospect’s challenges or issues.
- Then, they ask implication questions to explore the consequences of not addressing these problems.
- Finally, they use need-payoff questions to highlight the benefits of solving the issues.

By following this sequence, sales reps can understand the buyer’s needs. Today’s SPIN sellers ask fewer, more impactful questions and support their understanding with prior research.
SPIN selling is versatile and can complement other sales methodologies. It works best in complex sales, particularly when prospects aren’t yet aware of their challenges or the full impact of their situation. This customer-centric approach has made SPIN one of the most widely used sales methodologies worldwide.
Pros:
- Uses a structured approach to uncover customer needs
- Builds a strong foundation for consultative selling
- Encourages asking insightful questions
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming
12. Social Selling
Many of today’s buyers research social media first. Social selling leverages these platforms to find and engage potential customers. Sales reps build relationships and provide value through content and interactions.
In fact, according to a study by Forrester, 72% of B2B social sellers outperform peers who don’t use social. This shows the significant role social platforms play in the buyer’s journey.
Social selling is ideal for businesses looking to connect with their audience online.
Pros:
- Leverages social media to build relationships and generate leads
- Allows for targeted and personalized engagement
- Enhances brand visibility and credibility
Cons:
- It can be tricky to measure ROI directly
- Requires ongoing effort and consistency
13. Solution Selling
Solution selling was developed by Frank Watts in 1975 and refined by Mike Bosworth in the 1980s. It is perfect for handling complex sales. Instead of pushing products, solution salespeople act as consultants, diagnosing customer problems and recommending a customized mix of products to meet their needs. This method starts with a deep dive discovery to understand the prospect’s pain points.
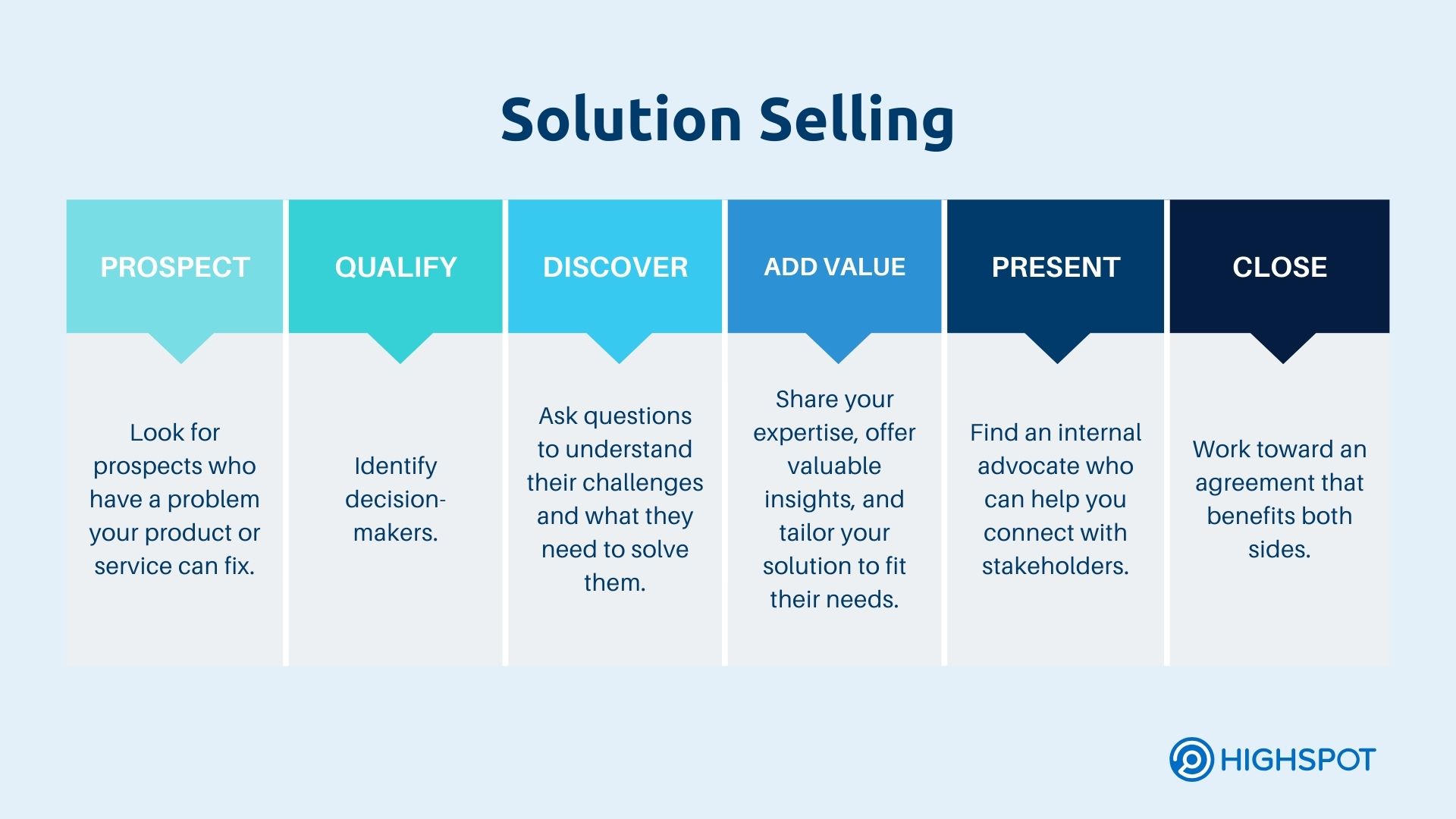
Chances are, prospects already have a good idea of what they need and are looking for the best fit, allowing reps to engage them deeply. Rather than just asking if the prospect is interested, sales reps share success stories to spark interest and show value right from the first touch. This sales approach builds credibility and shows the real impact of the solution.
Solution selling suits businesses that offer complex, customizable, or high-value products or services, such as SaaS, B2B, and financial services.
Pros:
- Focuses on providing personalized solutions
- Builds long-term relationships
- It can lead to higher-value deals
Cons:
- Requires deep understanding of the customer’s business and challenges
- Can be resource-intensive
- It may lead to over-customization and compromise efficiency
14. Target Account Selling
Target account selling (TAS) is a strategy designed to focus on pursuing the customer accounts with the highest potential fit for your products. It emphasizes quality over quantity using account targeting. TAS uses sales automation technology to spot buyer behaviors that signal a high-quality lead.
Target account selling identifies and selects target accounts based on specific criteria such as revenue, industry, geography, or business size. This ensures you focus on the most suitable accounts for your product. Sales reps then conduct thorough research and personalize their approach to build relationships. They identify key stakeholders and provide value through custom-nurturing activities and tailored content.
Pros:
- Focuses on high-value accounts and strategic opportunities
- Significantly improves brand reputation
- Less chances of getting rejected
Cons:
- Takes a lot of time to refine the account selection process
- It may lead to neglect of smaller or less strategic accounts
- Some accounts will still say no
15. Value Selling Framework
The ValueSelling Framework® is a dynamic selling methodology that ensures salespeople focus on engaging with qualified leads and selling the value of their products over just features or services. This framework emphasizes the importance of quickly qualifying buyers to generate a high-value sales pipeline.
Here’s how value-based selling works: Once sales managers and reps identify potential buyers, they assess whether these prospects are a good fit. They then take time to convey their product or solution’s unique value, demonstrating how it benefits the buyer’s specific needs. This approach helps develop mutually beneficial deals that are more likely to close.
The Value Selling Framework is suitable for various industries, buyer personas, and roles within a company. An entire organization can adopt this value-first methodology, creating a common language and strategy for the customer-facing team.
Pros:
- Provides a better understanding of how your product fits in various industries
- Helps justify premium pricing, offering a higher profit margin
- Builds customer loyalty
Cons:
- More beneficial for niche markets
- Competition is usually higher
16. Command of the Sale
Command of the Sale is a sales methodology from Force Management that empowers sales teams to take complete control of the sales process. This approach integrates the MEDDICC framework to focus on lead qualification and management from initial contact to deal closure.
This methodology defines clear accountability within the salesforce, ensuring everyone knows their role and masters the hand-off to the next department. This clarity creates a more consistent approach, with everyone speaking the same language when qualifying a deal and advancing it through each stage of the sales process.
Using MEDDICC, sales reps ask targeted questions to uncover customer needs, align solutions, and address objections early. This helps improve deal velocity, as everyone understands what’s required to move a deal forward.
Companies adopting this methodology often experience shorter sales cycles, higher conversion rates, and more accurate revenue projections, ultimately driving successful sales.
Pros:
- Emphasizes control and structure in the sales process
- Encourages accountability and performance tracking
Cons:
- Requires strong sales discipline
- May not allow for flexibility in different sales scenarios
How Do You Choose a Sales Methodology?
To find the best sales methodology for your business, consider three main elements:
- Strategy
- Product
- Customers
A suitable sales methodology will support these areas, helping you compete in a crowded market. So, which one will best support your sales strategy and help you achieve your ultimate goals?
Different methodologies are suited to various sales cycle lengths and customer engagement levels. For instance, some products are easy to sell in an online self-service marketplace, while more complex and expensive products require long sales cycles and personalized relationship-building.
Customer interaction is equally important. Each sales methodology favors a different type of engagement, and some can be more assertive than others. Think about how you want to connect with your customers and the experience you aim to create.
How to Implement a New Sales Methodology
Are you ready to add a proven sales methodology to your sales strategy? Here are a few steps to help with implementation:
Map Your Sales Process
Start by outlining your current sales cycle stages. This helps you incorporate the methodology into appropriate areas. For example, enhancements during the pain point discovery phase can help align solutions along the way. This often helps connect the feature to benefit dots for sales reps and customers.
Evaluate Sales Methodologies
Research and compare different methodologies and choose the one that fits your organization’s goals and initiatives. Remember, you are not limited to one methodology. You can mix and match concepts to create one that works for you, and a comprehensive sales training platform can assist with this customization. In some cases, this might mean using different methods for different sales teams.
As a rule of thumb, implementing a sales methodology takes at least six months or more. With strategic timing and clear communication highlighting the advantages for sales reps, you can lay the solid groundwork for successfully rolling out the new methodology.
Get Cross-Functional Buy-In
Ensure buy-in from major stakeholders across the business. Without cross-functional alignment on your sales methodology investment, you’ll face an uphill battle to deploy and adopt it.
There are four main groups you’ll want to focus on:
- Sales leaders
- Sales enablement
- Marketing
- Sales managers
Executive leadership must be aligned to champion your methodology internally and lead by example. Similarly, working with sales enablement ensures that your chosen methodology will be deeply embedded in your sellers’ daily workflows. Marketing, on the other hand, should be brought in so they can support sellers with the right sales content. Finally, your sales managers will make or break sales methodology deployment. They should believe in it, understand it, and know how to coach against it to successfully deploy a methodology within the business to ensure it sticks.
Examine Your Tech Stack
The key to ensuring your sales methodology is adopted is its availability within the tools your sellers use every day — from your CRM to your sales enablement platform. Work with your sales operations team to ensure that key guidance and training are available whenever reps need them so they can engage with customers effectively — and apply your chosen methodology during every conversation.
Embed the Methodology Across Your Organization
While a sales methodology aims to create a clear framework to help your reps effectively engage buyers, it’s not just for the sales team alone. It should be used by every part of your business, from the executive committee to product management. After all, every part of the organization should focus on the customer, and a unified methodology helps ensure that.
Begin training the executive leaders first, then cascade it down from upper management to frontline teams until they fully embrace it. Tailor the learning modules to different roles and ensure they communicate consistent messaging and terminology. Following this, conduct hands-on workshops and provide feedback and coaching sessions.
Related Resource: The Ultimate Guide to Sales Training
To keep the support strong, define metrics to track the impact of the new methodology. Regularly analyze sales performance data to identify areas for improvement and see to it that the methodology is driving the expected results.
By following these steps, you can implement a new sales methodology across your entire sales team and impact the entire sales funnel. This keeps everyone in sync and ensures a consistent customer experience, no matter the sales cycle stage.
Scale Your Sales Team With the Right Sales Methodology
Choosing the right sales methodology can feel overwhelming, with so many options and overlaps. This complexity is because sales tactics that worked decades ago don’t necessarily apply today. Buyers have evolved, products have become more complex, and selling methods have adapted. Today, information is easily accessible, eliminating the need for some traditional sales methods, like door-to-door sales.
The overlap in methodologies exists because buyers want solutions that simplify their lives, automate tasks, and support their workload. Sales reps must bridge the gap for prospects by using the right questions or providing third-party proof at the right time. These strategies can be the difference between closing a deal and losing a prospect.
Equip your sales reps with the best methodologies that support your sales process through Highspot. Request a demo today.





